Disease Overview
Canine adenovirus type 2 (CAV-2) is related to the hepatitis virus, canine adenovirus type 1 (CAV-1). CAV-2 is used in vaccines to provide protection against canine infectious hepatitis. CAV-2 is also one of the causes of infectious tracheobronchitis, also known as canine cough. 30
Merck Animal Health Solutions
For Canine Adenovirus Type 2
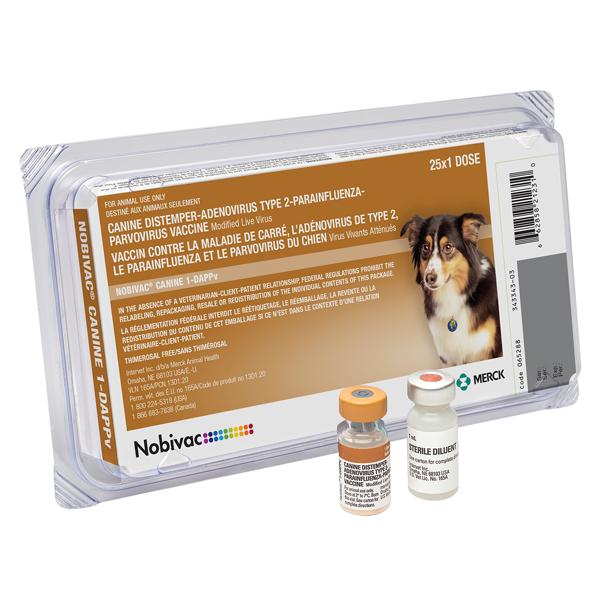
A vaccine recommended for use in healthy dogs as an aid in the prevention of disease caused by canine distemper virus, adenovirus type 1 (hepatitis) and adenovirus type 2 (respiratory disease), canine parainfluenza virus, and canine parvovirus.
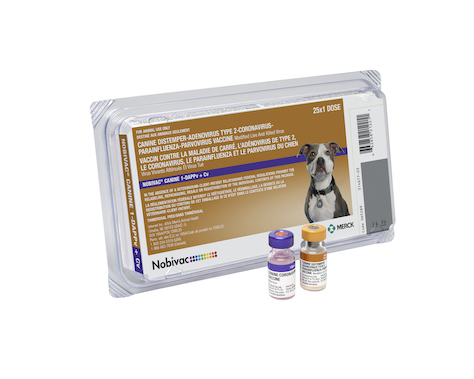
Recommended for the vaccination of healthy dogs as an aid in the prevention of disease caused by canine distemper virus, adenovirus type 1 (hepatitis), adenovirus type 2 (respiratory disease), canine parainfluenza virus, canine parvovirus, and canine coronavirus.
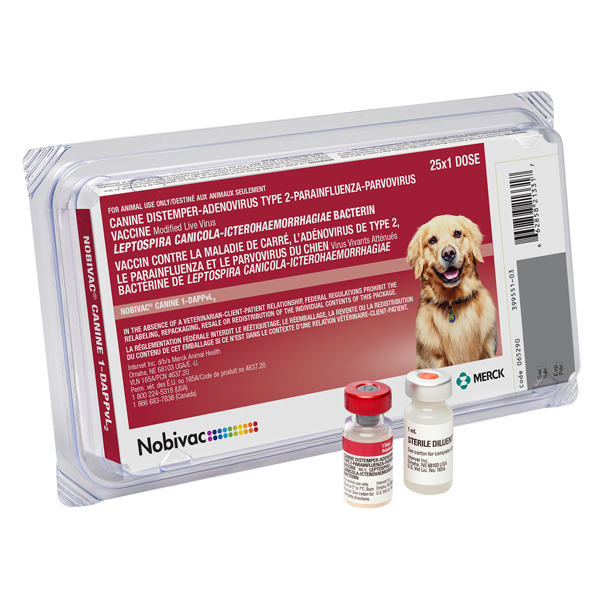
Recommended for the vaccination of healthy dogs as an aid in the prevention of disease caused by canine distemper virus, canine adenovirus type 1 (hepatitis), canine adenovirus type 2 (respiratory disease), canine parainfluenza virus, and canine parvovirus and against leptospiral disease due to L. canicola or L. icterohaemorrhagiae.
Recommended for the vaccination of healthy dogs as an aid in the prevention of disease caused by canine distemper virus, canine adenovirus type 1 (hepatitis), canine adenovirus type 2 (respiratory disease), canine coronavirus, canine parainfluenza virus, and canine parvovirus and against leptospiral disease due to L. canicola or L. icterohaemorrhagiae.
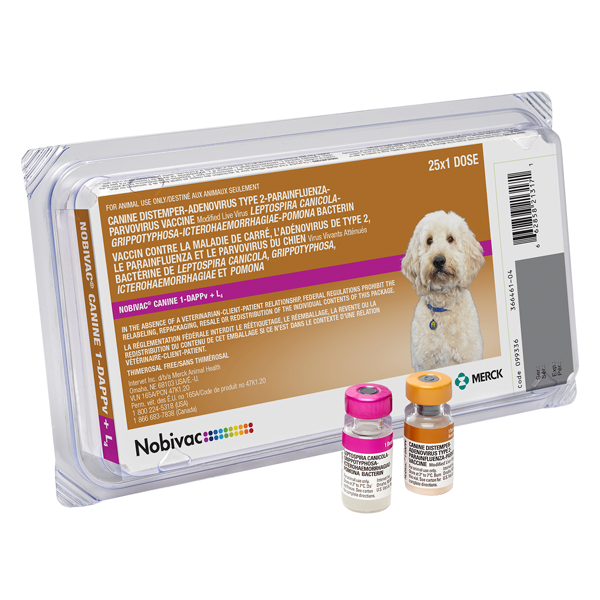
Recommended for the vaccination of healthy dogs as an aid in the prevention of disease caused by canine distemper virus, adenovirus type 1 (hepatitis), canine parainfluenza virus, and canine parvovirus. Additionally, it is an aid in the prevention of disease, urinary shedding and mortality caused by L. canicola, L. icterohaemorrhagiae, L. pomona, or L. grippotyphosa.
Recommended for the vaccination of healthy dogs for prevention of disease caused by canine distemper virus and canine parvovirus and as an aid in the prevention of disease caused by canine adenovirus (both infectious canine hepatitis and infectious tracheobronchitis) for up to 3 years following initial and booster vaccinations.
An intranasal vaccine shown to be effective for vaccination of healthy dogs 3 weeks of age or older against canine adenovirus type 2, canine parainfluenza virus, and Bordetella bronchiseptica.
An intranasal vaccine shown to be effective for vaccination of healthy dogs 3 weeks of age or older against canine adenovirus type 2, canine parainfluenza virus, and Bordetella bronchiseptica.
Transmission
Adenoviruses are spread directly from dog to dog through infected respiratory secretions or by contact with contaminated feces or urine.
Clinical Signs 30
Respiratory disease (CAV-2)
- Dry, hacking cough (dogs)
- Retching
- Sneezing
- Watery nasal discharge
- Pneumonia, inappetence, fever, and lethargy in severe cases
Hepatitis (CAV-1)
- Fever
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Risk Factors
- Dogs that come from shelters, rescue centers, breeding kennels, or pet stores
- Boarding at a kennel or doggie daycare
- Visiting groomers, dog parks, or engaging with other dogs on a daily basis
- Dogs that live in multi-pet homes
References:
1. Greene C. Infectious canine hepatitis and canine acidophil cell hepatitis. In: Greene CE, ed. Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Saunders/Elsevier; 2006:43.