Disease Overview
This is associated with enterotoxemia in cattle, and is also known as overeating disease. It is common in older calves that eat a high grain diet.
Merck Animal Health Solutions
For Clostridium perfringens D

For use in healthy swine as an aid in the control of ileitis caused by Lawsonia intracellularis, an aid in the reduction of colonization by Lawsonia and an aid in the reduction of duration of fecal shedding. Duration of immunity for at least 20 weeks has been demonstrated.
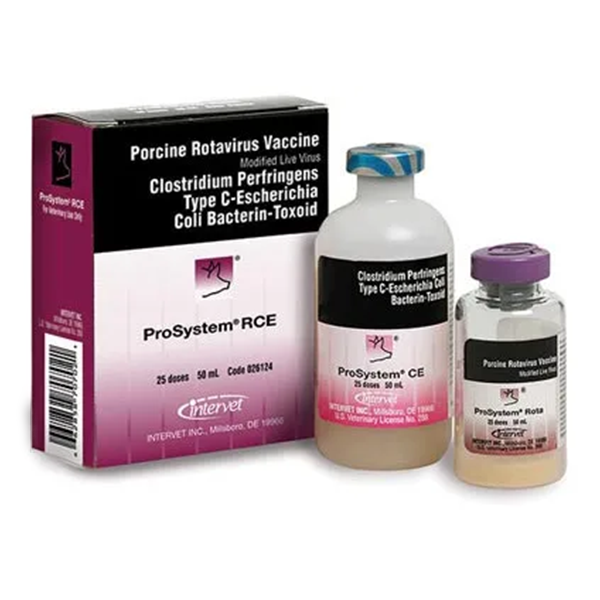
An aid in prevention of rotaviral diarrhea, enterotoxemia and colibacillosis in nursing pigs of vaccinated sows/gilts. Unique rotavirus and seven-way scours protection. Includes two major rotavirus serotypes G4 and G5 of Serogroup A. Freeze-dried MLV vaccine with bacterin/toxoid diluent.

A vaccine that offers the trusted clostridial disease prevention of Vision 7 combined with protection against pinkeye caused by Moraxella bovis in a convenient 2 mL dose powered by the SPUR® adjuvant.
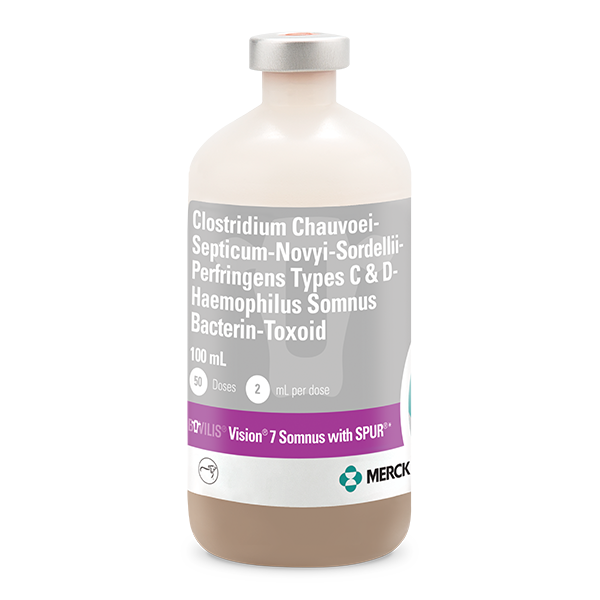
CLOSTRIDIUM CHAUVOEI-SEPTICUM-NOVYI-SORDELLII-PERFRINGENS TYPES C & D HAEMOPHILUS SOMNUS BACTERIN-TOXOID

CLOSTRIDIUM CHAUVOEI-SEPTICUM-NOVYI-SORDELLII-PERFRINGENS TYPES C & D BACTERIN-TOXOID

CLOSTRIDIUM CHAUVOEI-SEPTICUM-HAEMOLYTICUM-NOVYI-SORDELLII-PERFRINGENS TYPES C & D-HAEMOPHILUS SOMNUS BACTERIN-TOXOID

CLOSTRIDIUM CHAUVOEI-SEPTICUM-HAEMOLYTICUM-NOVYI-SORDELLII-PERFRINGENS TYPES C & D BACTERIN-TOXOID
Clinical Signs
- Sudden deaths in best-conditioned animals
- Circling
- Pushing against fixed objects
- Convulsions


